How to operate a drone? It’s a question many ask, intrigued by the possibilities of aerial flight. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from understanding basic components and safety protocols to mastering advanced flight techniques and exploring the legal aspects. We’ll cover everything from pre-flight checks and essential maneuvers to capturing stunning aerial photography and videography.
Prepare for takeoff!
Whether you’re a complete novice or seeking to enhance your existing skills, this comprehensive resource equips you with the knowledge and confidence to safely and effectively pilot your drone. We’ll break down complex concepts into easily digestible steps, ensuring a smooth and enjoyable learning experience.
Drone Components and Terminology
Understanding the basic components of a drone and their functions is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section will cover the key parts of a typical drone, along with a glossary of common terms used in drone piloting.
Major Drone Components and Their Functions
A drone’s functionality relies on the coordinated operation of several key components. These include:
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate the thrust necessary for lift and maneuverability. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of thrust and efficiency.
- Motors: Electric motors power the propellers, converting electrical energy into rotational motion. Brushless motors are commonly used in drones for their efficiency and longevity.
- Flight Controller: This is the drone’s “brain,” responsible for processing data from various sensors and controlling the motors to maintain stability and execute flight commands. It integrates data from the GPS, IMU, and other sensors.
- Battery: Provides the power for the motors and other onboard electronics. The battery’s capacity directly impacts flight time.
- GPS Module: Allows the drone to determine its location and maintain its position. Essential for features like Return-to-Home (RTH) and waypoint navigation.
- IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit): Measures the drone’s orientation and movement, providing data to the flight controller for stabilization.
- Remote Controller: Allows the pilot to control the drone’s movement and functions.
- Camera (optional): Captures images and videos from an aerial perspective.
Drone Terminology
Familiarizing yourself with common drone terminology is essential for understanding flight instructions and troubleshooting issues.
- Yaw: Rotation of the drone around its vertical axis (spinning left or right).
- Pitch: Rotation of the drone around its lateral axis (tilting forward or backward).
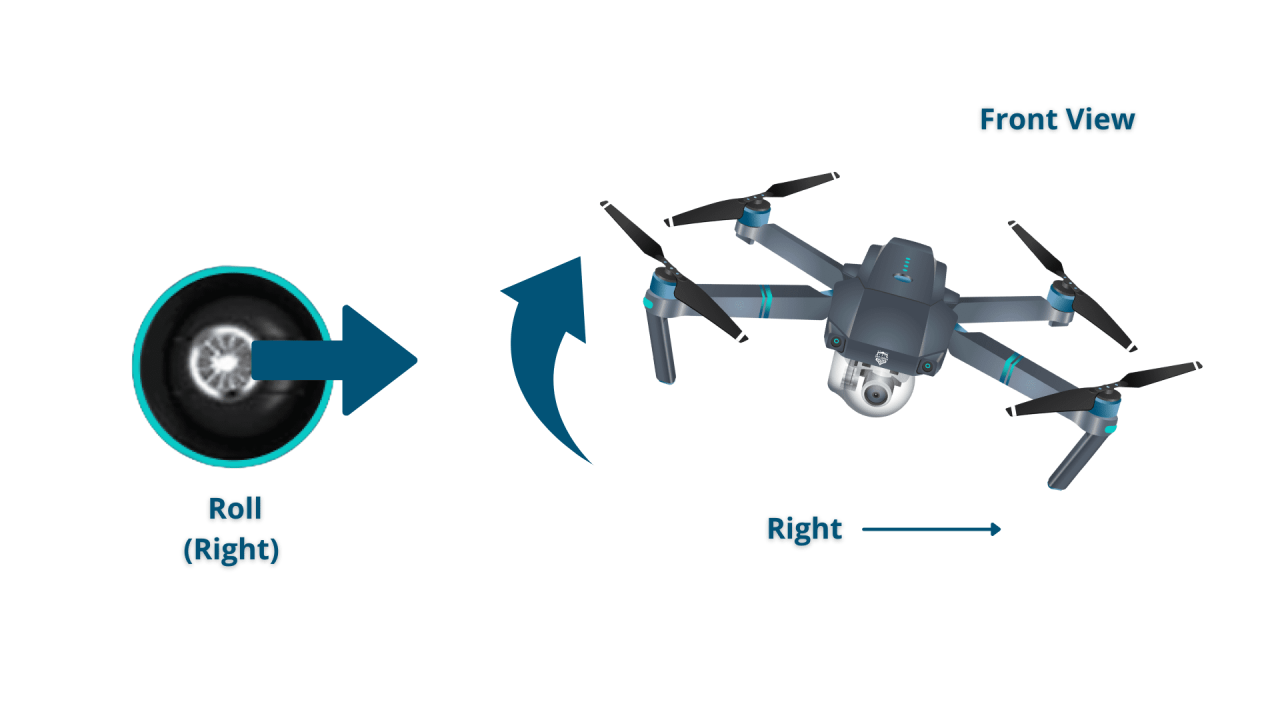
- Roll: Rotation of the drone around its longitudinal axis (tilting left or right).
- Throttle: Controls the drone’s altitude; increasing throttle causes ascent, decreasing throttle causes descent.
- Altitude Hold: A flight mode that maintains a constant altitude, even with slight variations in throttle input.
Drone Battery Comparison
Different drone batteries offer varying performance characteristics. The following table provides a comparison of common battery types:
| Battery Type | Voltage (V) | Capacity (mAh) | Approximate Flight Time (minutes) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LiPo 3S 11.1V 1500mAh | 11.1 | 1500 | 15-20 |
| LiPo 4S 14.8V 2200mAh | 14.8 | 2200 | 25-30 |
| LiPo 6S 22.2V 5200mAh | 22.2 | 5200 | 40-50 |
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight checklist and adherence to safety procedures are paramount. This ensures the safe and responsible operation of your drone.
Pre-Flight Checklist
A comprehensive pre-flight checklist should include:
- Battery Check: Ensure the battery is fully charged and properly connected.
- Propeller Inspection: Check for damage or looseness. Replace damaged propellers.
- GPS Signal Verification: Ensure the drone has a strong GPS signal before takeoff. The number of satellites acquired should be sufficient for stable flight.
- Gimbal Check (if applicable): Ensure the gimbal is functioning correctly and securely mounted.
- Remote Controller Check: Verify the remote controller is fully charged and properly paired with the drone.
- Visual Inspection: Conduct a visual inspection of the drone for any damage or loose components.
- Flight Area Assessment: Check for obstacles, people, and other potential hazards in the flight area.
Safety Procedures
Essential safety procedures for drone operation include:
- Choosing Appropriate Flight Locations: Select open areas away from obstacles, people, and populated areas. Avoid flying near airports or other restricted airspace.
- Respecting Airspace Regulations: Familiarize yourself with and adhere to all local and national airspace regulations. Obtain necessary permits or licenses if required.
- Understanding Emergency Protocols: Know how to perform an emergency landing in case of technical difficulties or loss of control. Practice emergency procedures in a safe environment.
- Maintaining Visual Line of Sight: Always maintain visual contact with the drone during flight. Do not fly beyond your visual range.
- Weather Considerations: Avoid flying in adverse weather conditions such as strong winds, rain, or snow.
Safe Drone Launch and Landing Flowchart
The following flowchart illustrates the steps involved in a safe drone launch and landing:
(Note: A visual flowchart would be included here. The steps would be described in detail, illustrating the pre-flight checks, launch sequence, flight operation, and safe landing procedures.)
Basic Flight Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding basic flight controls is the foundation of safe and effective drone piloting. This section will cover the functions of control sticks and steps for performing basic maneuvers.
Drone Remote Control Functions

Most drone remotes use two control sticks: one for controlling the drone’s pitch and roll (movement forward, backward, left, and right), and the other for controlling yaw and throttle (rotation and altitude). Buttons on the remote often control additional functions such as camera settings and Return-to-Home (RTH).
Basic Flight Maneuvers
Here are step-by-step instructions for performing basic flight maneuvers:
- Hovering: Gently adjust the throttle and control sticks to maintain a stable position in the air.
- Ascending: Increase the throttle to raise the drone’s altitude.
- Descending: Decrease the throttle to lower the drone’s altitude.
- Moving Forward/Backward: Gently push the control stick forward to move the drone forward and backward to move it backward.
- Moving Left/Right: Gently push the control stick left or right to move the drone laterally.
- Yawing: Rotate the yaw control stick to turn the drone left or right.
Maintaining Stable Flight
Tips for maintaining stable flight and avoiding common piloting errors include:
- Smooth and Gradual Control Inputs: Avoid jerky movements of the control sticks.
- Practice in a Safe Environment: Practice your piloting skills in a large, open area with minimal obstacles.
- Understand Wind Conditions: Adjust your control inputs to compensate for wind.
- Pay Attention to Battery Level: Monitor the battery level and return the drone to land before the battery is critically low.
Advanced Flight Techniques
Once comfortable with basic flight controls, you can explore more advanced techniques to enhance your drone operation and capture stunning aerial footage.
Advanced Flight Modes and Features
Many drones offer various flight modes, including:
- Waypoint Navigation: Allows you to pre-program a flight path with multiple waypoints, enabling automated flight along a defined route.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): This automated feature guides the drone back to its takeoff point, typically using GPS data. It is a crucial safety feature.
- Follow Me Mode: The drone automatically follows a designated subject (e.g., a person or vehicle).
- Point of Interest (POI): The drone orbits a specific point, keeping it centered in the frame.
Planning and Executing Complex Flight Paths
Planning a complex flight path involves selecting waypoints, considering obstacles, and programming the drone’s flight path using the drone’s software or app. Accurate planning is crucial to avoid collisions and ensure a smooth flight.
Aerial Photography and Videography
Advanced techniques for aerial photography and videography include using specific flight modes (like POI or Follow Me), adjusting camera settings (aperture, shutter speed, ISO), and composing shots to create visually appealing content. Understanding light conditions and composition is essential for capturing high-quality images and videos.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and the ability to troubleshoot common problems are essential for extending the lifespan and performance of your drone.
Routine Maintenance Tasks
Routine maintenance tasks include:
- Cleaning Propellers: Regularly clean propellers to remove dirt and debris.
- Checking Motor Mounts: Inspect motor mounts for any signs of damage or looseness.
- Calibrating Sensors: Periodically calibrate the drone’s sensors (IMU, compass) to ensure accurate readings.
- Battery Care: Store batteries properly and avoid extreme temperatures.
- Inspecting the Airframe: Regularly inspect the drone’s body for any damage or wear and tear.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
Here is a table listing common drone problems, their causes, and recommended solutions:
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Low Battery Warning | Low battery charge | Charge the battery or land the drone immediately. |
| GPS Signal Loss | Obstructed GPS signal, weak signal | Relocate to an area with a clear view of the sky. |
| Motor Malfunction | Motor damage, loose connection | Inspect motors and connections; replace damaged components. |
| Drone Drift | Calibration issues, wind | Calibrate the drone’s sensors; adjust flight parameters to compensate for wind. |
Legal and Regulatory Compliance (Example: United States)
Operating a drone requires adherence to specific laws and regulations. This section will provide an overview of regulations in the United States. Remember to check your local regulations for your specific area.
US Drone Regulations, How to operate a drone
In the United States, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) regulates drone operation. Key regulations include:
- Registration: Most drones must be registered with the FAA.
- Certification: Depending on the drone’s use and weight, a Remote Pilot Certificate may be required.
- Airspace Restrictions: Flying near airports, restricted airspace, or over populated areas is often prohibited.
- Visual Line of Sight: Maintaining visual line of sight with the drone is generally required.
- Operating Limits: There are restrictions on the maximum altitude and distance a drone can fly.
Obtaining Permits and Licenses
The process of obtaining necessary permits or licenses involves registering your drone with the FAA and, depending on your intended use, obtaining a Remote Pilot Certificate. The FAA website provides detailed information on the registration and certification processes.
Restricted Drone Operation Scenarios
Drone operation is often restricted or prohibited in the following scenarios:
- Near airports or military bases.
- Over crowds or densely populated areas.
- In national parks or other protected areas without permission.
- During adverse weather conditions.
- Without proper registration or certification.
Drone Photography and Videography
Drones offer unique perspectives for capturing stunning photos and videos. Understanding camera settings and composition techniques is key to producing high-quality aerial content.
Drone Camera Settings
Drone cameras typically allow adjustments to:
- Aperture: Controls the amount of light entering the camera.
- Shutter Speed: Determines the length of time the camera’s sensor is exposed to light.
- ISO: Measures the camera’s sensitivity to light.
- White Balance: Adjusts the color temperature to ensure accurate color reproduction.
Shot Composition and Planning
Planning your shots involves considering:
- Lighting: The best time to shoot is during the golden hour (sunrise and sunset) for optimal lighting.
- Angle and Perspective: Experiment with different angles and perspectives to create unique shots.
- Subject Placement: Consider the rule of thirds to create balanced and visually appealing compositions.
- Background Elements: Pay attention to the background to avoid distracting elements.
Capturing High-Quality Photos and Videos
To capture high-quality aerial photos and videos:
- Choose the right time of day for optimal lighting.
- Plan your shots and composition carefully.
- Adjust camera settings for the specific conditions.
- Use smooth and controlled movements.
- Review and edit your footage.
Illustrative Examples of Drone Use Cases: How To Operate A Drone
Drones are finding applications across various industries. Here are three examples demonstrating the versatility of drone technology.
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and enjoyable drone operation.
Agriculture: Crop Monitoring and Precision Farming
Drones equipped with multispectral cameras can capture detailed images of crops, allowing farmers to monitor crop health, identify areas needing attention, and optimize resource allocation. This leads to increased yields and reduced input costs.
Using drones for crop monitoring allows farmers to identify issues early, preventing significant yield losses and saving resources. However, initial investment in drones and software can be substantial.
Learning to fly a drone involves understanding its controls and mastering basic maneuvers. A crucial step is familiarizing yourself with safety regulations and best practices. For a comprehensive guide on the subject, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced flight techniques. Successfully operating a drone requires practice and a commitment to safety.
Construction: Site Surveying and Progress Monitoring

Drones provide a cost-effective and efficient way to survey construction sites, monitor progress, and identify potential problems. High-resolution imagery and 3D models generated from drone data can aid in planning and project management.
Drone surveys significantly reduce the time and cost associated with traditional surveying methods. However, weather conditions can impact data acquisition and the expertise to process the data is necessary.
Real Estate: Property Photography and Virtual Tours
Drones offer stunning aerial views of properties, enhancing marketing materials and attracting potential buyers. Virtual tours created using drone footage provide immersive experiences for prospective clients.
Drone photography significantly enhances property listings, showcasing properties from unique perspectives and attracting more buyers. However, regulations regarding airspace and privacy must be strictly adhered to.
Mastering drone operation is a rewarding journey, opening up a world of exciting possibilities. From breathtaking aerial photography to efficient surveying, the applications are vast and varied. Remember to always prioritize safety, adhere to regulations, and continuously refine your skills. With practice and a thorough understanding of the principles Artikeld here, you’ll be confidently soaring through the skies in no time.
Safe flying!
Common Queries
What type of drone is best for beginners?
User-friendly drones with GPS, return-to-home (RTH) features, and beginner-friendly flight modes are ideal for novices. Look for models with stability assist and intuitive controls.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model, battery size, and flight conditions. Check the manufacturer’s specifications for estimated flight times.
What happens if I lose GPS signal?
Many drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function that will automatically guide the drone back to its starting point if GPS signal is lost. However, always keep your drone within visual line of sight.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements vary by country and region. Check with your local aviation authority for specific regulations and registration procedures.
